Managing waste is a daily challenge in factories, municipalities, housing projects, and commercial facilities. Bold Waste Shredder Machine breaks this cycle by cutting disposal costs, increasing recycling rates, and reducing the amount of material that ends up in landfills. Herein, we describe how shredding works in real industrial settings, the types of systems used, and the cost benefits for plants that want to reduce waste volumes without introducing additional work.
Overview: Waste Shredder Machine
- A waste Shredder Machine reduces Waste volume, increases transport efficiency, and supports landfill diversion strategies.
- The plants adopt an industrial shredder machine system to reduce hauling charges and increase recycling options.
- The dual-shaft and twin-shaft shredder design can handle mixed waste streams more efficiently.
- For uniform materials such as plastics and textiles, a single-shaft shredder is suitable.
- Leading Shredder Machine Manufacturer provides energy-efficient drives and long-life blades.
- Businesses utilize shredders in conjunction with broader landfill diversion solutions to achieve their sustainability goals.
Why Shredding Matters for Modern Waste Systems
Waste is no longer just a matter of volume anymore. It becomes an operational expense. Rising disposal charges, transport charges, and landfill limits force organisations to find practical ways of managing waste. One of the best tools in this shift has been shredding. These are the reasons why businesses use a waste Shredder Machine today:
- Reduces bulky waste to uniform pieces that are easier to store, handle, and transport.
- Increase container fill efficiency – more waste per trip & fewer lorry movements.
- Low transport frequency reduces monthly hauling costs for bulky waste.
- Improved workflow on sorting lines with a reduction of jams, stoppages & manual intervention.
- Supports smoother waste processing of packaging scrap, production rejects, and warehouse disposals.
- Transforms a laborious and inconsistent process into a cleaner, predictable, and more economical waste handling system.
How a Waste Shredder Machine Reduces Landfill Volume
With landfill space being squeezed and regulations tightening, reducing waste sent to disposal sites is a top priority. A waste Shredder Machine reduces this pressure by shredding Waste at the source. Why shredding lowers landfill dependence:
- Valves in systems like dual shaft shredder or twin shaft shredder are collapsed, and material density is increased.
- Produces smaller batches that use less space and reduces total landfill contributions.
- Offers uniform, consistent fragments for downstream sorting lines.
- Cleaner, prepared streams let recyclers recover more plastics, cardboard & metals!
- Adds value to recyclables that offsets the cost of operating or buying shredding equipment/machinery.
- Reduces waste volume by 20-50% depending on material type and shred size, resulting in fewer bins, more floor space, and a predictable disposal schedule.
Industrial waste handling demands the right shredding partner; this article reveals what separates top manufacturers from the rest.
Applications in Industrial & Commercial settings
Waste is produced differently in every facility, so selecting the right waste Shredder Machine depends on the material, the operation speed, and output requirements. The goal is not to destroy waste but to match the machine to the environment so the workflow is smoother and more economical. Common real-world applications include:
- Handling of municipal and Facility wastes: Mixed waste from commercial buildings, housing communities, and institutional campuses often contains packaging, light debris, and daily disposals. Her,e multimaterial shredders trim bulk volume so containers fill equally and transport cycles drop.
- Manufacturing & Production Lines: Plants that process consistent scrap offcuts, defective batches, trimmings, or textiles may use shredders to reduce pile-ups, clear floor space, and prepare waste for recycling or energy recovery systems.
- Warehousing & Logistics Operations: Goods damaged or returned occupy valuable storage space, as does old packaging. Shredding converts these items into more easily transportable and storable fractions.
- Recycle & Material Recovery Facilities: The pre-shredding increases the efficiency of the downstream sorting lines. Uniform fragments enable faster operation of optical sorters, magnets, and density separators, resulting in higher recovery rates of plastics, cardboard & metals.
- Electronic Waste Processing: As electronics become increasingly discarded, dedicated electronic waste shredders dismantle cables, boards, and other small devices to facilitate the safe separation of metals, plastics & recoverable components.
- Industrial Waste Streams: Factories handling mixed industrial waste. Bulky rejects, packaging blocks, and old inventory use the waste Shredder Machine to stabilize waste flow and avoid manual intervention during disposal.
Before buying a twin-shaft shredder machine, it’s important to assess not just the purchase price but the long-term ROI. This India-specific guide walks you through it.
Energy Use and Cost Considerations
Knowing how a waste Shredder Machine uses energy helps plants compare operating costs to long-term financial return. Factors such as machine type, feed material, and throughput affect the energy profile.
Energy Consumption Factors
- Material Throughput: kWh/tonne is dependent on the speed and quantity of material entering the shredder.
- Feed Material Type: Tougher or mixed waste increases torque, resulting in a higher power draw.
- Motor and Drive Design: Efficient motors, high-quality cutters, and variable-speed drives ensure consistent usage.
- Batch Behaviour: The consistency with which the machine runs depends on moisture, density, and particle size.
- Budget Planning: Predictable energy patterns help facilities avoid surprises in monthly operating costs.
Where the Financial Savings Come From
- Lower Transport Volume: Shredded waste uses less space and reduces the number of trips.
- Improved Recycling Value: Cleaner, uniform fragments are easier to recover and sell.
- Reduced Labour Hours: Less manual sorting & fewer workflow interruptions, lower staffing costs.
- Integrated System Gains: Pairing a shredder with a conveyor, separator, or baler multiplies savings along the entire waste line.
- Faster Payback Period: Reductions in handling, transport, and disposal expenditures outweigh operating costs.
Choosing the Right Shredder Machine Manufacturer
The right waste shredder machine supplier influences performance, maintenance, energy use, and long-term reliability. A strong manufacturer matches your machine to your waste stream to avoid downtime. Checklist of points to consider before choosing a supplier:
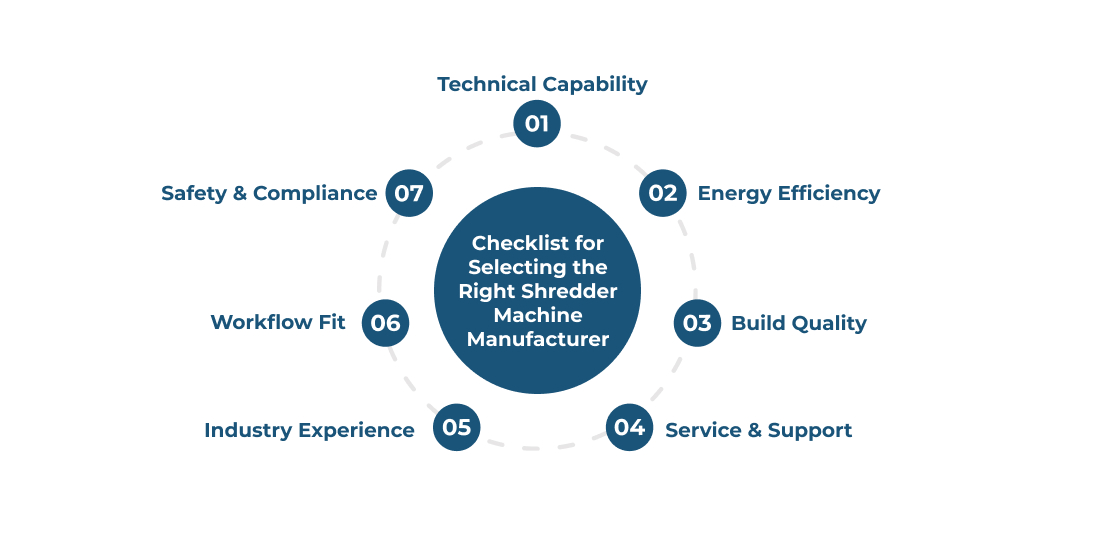
- Technical Capability: Check throughput ratings, rotor design (single shaft, dual shaft/twin shaft), and whether the machine can handle your waste.
- Energy Efficiency: Look at motor performance, drive technology, and expected kWh/tonne usage for realistic budgeting.
- Build Quality: Look for tough blades, frames, stable gearboxes, and parts built for continuous operation.
- Service & Support: Get quick access to spares, rapid technician response times, and clear warranty terms.
- Industry Experience: Prefer manufacturers having installations in similar sectors and with experience in handling mixed, packaging/industrial waste.
- Workflow Fit: Choose systems that integrate with conveyors, balers, or sorting equipment without major layout changes.
- Safety & Compliance: Confirm safety standards and automation features availability, such as sensors and load monitoring.
Common Considerations for Buyers
Before investing in a waste shredder machine, buyers typically focus on more than capacity numbers. They want to know how the machine fits their waste stream. An operational bottleneck is avoided later due to a practical evaluation. Key factors buyers look at:
- Material Behaviour: How your waste behaves during shredding. Whether it compresses, splinters, or tangles determines the right rotor and cutter setup.
- Space Planning: Floor space, feeding access & discharge height checks ensure the shredder fits in your existing layout.
- Maintenance: Access to blades, screens & service panels reduces downtime & simplifies routine checks.
- Noise & Dust Control: Buyers often verify whether the system requires enclosures, extraction units, or noise-reduction panels for safe working conditions.
- Operator Training: Daily handling, safety protocol, and troubleshooting should be a confidence factor in the long-term machine performance.
- Future Scalability: Choosing a setup with the possibility of adding conveyors, balers, and sorting attachments allows growth without removing the core machine.
Conclusion: Why Shredding Makes Sense for Long-Term Waste Control
Using a waste Shredder Machine enables organisations to reduce waste-handling costs at the source, increase recycling potential, and improve Waste handling routines. With the proper rotor design and process capacity, shredding is a proven part of an environmental and operational strategy for a facility.
EnvCure Technocrat LLP, one of the leading waste shredder machine manufacturers in India, supports industries across India with Waste Recycling Shredder Machine systems, conveyors, composting units, and turnkey waste-processing solutions. Its focus is on reliability, service support, and easy integration into existing workflows, helping facilities reduce waste volume, recycle more, and optimise long-term disposal costs. Organisations upgrading or expanding waste handling operations can contact EnvCure for recommendations and projected savings on the basis of real operating conditions.
FAQs Related to Waste Shredder Machine
Q. How does a waste shredder machine reduce landfill volume?
Ans: By cutting bulky items into smaller, denser pieces that compact more efficiently and take up less space in transport and landfill, shredders lower the physical volume sent for disposal.
Q. How much can I save on disposal costs using a shredder?
Ans: Savings come from reduced transport volume, lower landfill fees, and increased recycling revenue; exact savings depend on waste mix, volumes, and local disposal rates, but many businesses report significant monthly reductions.
Q. How do I choose the right shredder capacity for my facility?
Ans: Estimate daily/weekly waste tonnage, feed material type, desired output size, and uptime needs, then match to throughput (tph or kg/hr) and rotor design; ask suppliers for test cuts with your waste.
Q. Can shredded waste be sold or recycled to generate revenue?
Ans: Yes, shredded materials (plastics, metals, paper, organics for composting) often fetch higher recovery rates and sometimes direct resale value; revenue depends on material quality and market demand.
Q. What types of waste can a waste shredder process?
Ans: Industrial shredders handle plastics, wood, paper/cardboard, textiles, rubber, metals (light scrap), electronic waste, and many organic/municipal streams, depending on the model and rotor design.









